1、数组创建
np.set_printoptions(precision=6, linewidth=320, suppress=True, threshold=np.inf)
# 生成[0,1)之间的数据
np.random.random(10)
np.random.rand(4, 2)
np.random.rand(4, 3, 2)
# 标准正态分布
np.random.randn(2, 4)
# Two-by-four array of samples from N(3, 6.25)
2.5 * np.random.randn(2, 4) + 3
# 随机整数,范围区间为[low,high)
np.random.randint(-5, 5, size=(2,2))
# arange类似于range函数,只不过返回的不是列表,而是数组
# arange允许非整数值输入,产生一个非整型的数组
>>> m = np.array([np.arange(2), np.arange(2)])
>>> m.ndim # num of dimensions/axes
2
>>> m.shape
(2, 2)
>>> m.dtype #数组元素类型
>>> m.itemsize # 每个元素占字节数
>>> m.nbytes # 所有元素占的字节
>>> m.size # 数组元素数
>>> a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
>>> a[0,1]
2
>>> np.zeros(10)
array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
>>> np.zeros((2,3))
array([[ 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0.]])
>>> np.empty((2,3))
array([[ 7.70742408e-322, 0.00000000e+000, 2.78145267e-307],
[ 4.00537061e-307, 2.23419104e-317, 0.00000000e+000]])
# linspace(start, stop, N) 产生N个等距分布
>>> np.linspace(0, 1, 5)
array([ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ])
>>> np.logspace(0, 1, 5) # 产生N个对数等距分布
array([1., 1.77827941, 3.16227766, 5.62341325, 10.])
>>> x_ticks = np.linspace(-1, 1, 5)
>>> y_ticks = np.linspace(-1, 1, 5)
# r_ / c_ 来产生行向量或者列向量
>>> np.r_[0:1:.1]
array([ 0. , 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9])
>>> np.r_[(3,22,11), 4.0, [15, 6]]
array([3., 22., 11., 4., 15., 6.])
>>> np.c_[1:3:5j]
array([[ 1. ],
[ 1.5],
[ 2. ],
[ 2.5],
[ 3. ]])
2、numpy数据类型
>>> np.float64(42)
42.0
>>> np.int8(42.0)
42
>>> np.bool(42)
True
>>> np.arange(7, dtype=np.uint16)
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], dtype=uint16)
# 类型转换
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
float_arr = arr.astype(np.float64)
numeric_strings = np.array(['1.25', '-9.6', '42'], dtype=np.string_)
numeric_strings.astype(float)
# 编码转换 Encode words as UTF-8
>>> wordsList = [word.decode('UTF-8') for word in wordsList]
3、索引与切片
>>> a = np.arange(9)
>>> a[:7:2]
array([0, 2, 4, 6])
>>> a[::-1]
array([8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0])
>>> s = slice(3,7,2)
>>> a[s]
array([3, 5])
# 非零元素索引
>>> np.nonzero(a)
>>> b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4)
>>> b
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
>>> b[:,0,0]
array([ 0, 12])
>>> b[0, :, :]
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
>>> b[0, ...]
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
>>> b[0,1]
array([4, 5, 6, 7])
>>> b[...,1]
array([[ 1, 5, 9],
[13, 17, 21]])
>>> b[:,1]
array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[16, 17, 18, 19]])
>>> b[0,:,1]
array([1, 5, 9])
>>> b[0,:,-1]
array([ 3, 7, 11])
>>> b[0,::2,-1]
array([ 3, 11])
#花式索引
arr = np.empty((8, 4))
for i in range(8):
arr[i] = i
>>> arr[[4, 3, 0, 6]]
>>> arr[[-3, -5, -7]]
>>> b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4)
>>> b
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
# ravel返回视图,对视图所做的修改会影响原始矩阵
>>> b.ravel()
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23])
# flatten返回拷贝,对拷贝所做的修改不会影响原始矩阵
>>> b.flatten()
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23])
>>> b.transpose()
>>> b.resize((2,12))
>>> b
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]])
4、数组拼接
>>> a = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3)
>>> b = 2 * a
>>> np.hstack((a, b))
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 4],
[ 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10],
[ 6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 16]])
>>> np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1)
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 4],
[ 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10],
[ 6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 16]])
>>> np.vstack((a, b))
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 0, 2, 4],
[ 6, 8, 10],
[12, 14, 16]])
>>> np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0)
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 0, 2, 4],
[ 6, 8, 10],
[12, 14, 16]])
>>> np.dstack((a, b))
array([[[ 0, 0],
[ 1, 2],
[ 2, 4]],
[[ 3, 6],
[ 4, 8],
[ 5, 10]],
[[ 6, 12],
[ 7, 14],
[ 8, 16]]])
>>> oned = np.arange(2)
>>> twice_oned = 2 * oned
>>> np.column_stack((oned, twice_oned))
array([[0, 0],
[1, 2]])
>>> np.row_stack((oned, twice_oned))
array([[0, 1],
[0, 2]])
>>> a = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)
>>> np.hsplit(a, 3)
[array([[0],
[3],
[6]]), array([[1],
[4],
[7]]), array([[2],
[5],
[8]])]
>>> np.split(a, 3, axis=1)
[array([[0],
[3],
[6]]), array([[1],
[4],
[7]]), array([[2],
[5],
[8]])]
>>> np.vsplit(a, 3)
[array([[0, 1, 2]]), array([[3, 4, 5]]), array([[6, 7, 8]])]
# stack()增加维度
a=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
b=np.array([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
a
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
b
array([[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]])
np.stack([a, b], axis=0)
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]]])
np.stack([a, b], axis=1)
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 7, 8, 9]],
[[ 4, 5, 6],
[10, 11, 12]]])
np.stack([a, b], axis=2)
array([[[ 1, 7],
[ 2, 8],
[ 3, 9]],
[[ 4, 10],
[ 5, 11],
[ 6, 12]]])
5、数组增加一维
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.random.rand(4)
>>> a
array([0.153286, 0.78193 , 0.813937, 0.211314])
>>> a[np.newaxis, ...]
array([[0.153286, 0.78193 , 0.813937, 0.211314]])
>>> a[np.newaxis, :]
array([[0.153286, 0.78193 , 0.813937, 0.211314]])
>>> a[:, np.newaxis]
array([[0.153286],
[0.78193 ],
[0.813937],
[0.211314]])
>>> np.expand_dims(a, axis=0)
array([[0.153286, 0.78193 , 0.813937, 0.211314]])
>>> np.expand_dims(a, axis=1)
array([[0.153286],
[0.78193 ],
[0.813937],
[0.211314]])
>>> np.reshape(a, (-1, 1))
array([[0.153286],
[0.78193 ],
[0.813937],
[0.211314]])
>>> b = np.reshape(a, (-1, 1))
>>> np.squeeze(b, axis=1)
array([0.153286, 0.78193 , 0.813937, 0.211314])
6、where
>>> xarr = np.array([1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5])
>>> yarr = np.array([2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5])
>>> cond = np.array([True, False, True, True, False])
>>> np.where(cond, xarr, yarr)
array([ 1.1, 2.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.5])
>>> np.where(arr > 0, 2, -2)
array([2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
>>> np.where(arr > 0, 2, arr)
array([2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
7、数组前一项减去后一项
od = np.array([21000, 21180, 21240, 22100, 22400])
dist = od[1:] - od[:-1]
8、数组排序
names = np.array(['bob', 'sue', 'jan', 'ad'])
weights = np.array([20.8, 93.2, 53.4, 61.8])
weights.sort()
ordered_indices = np.argsort(weights)
weights[ordered_indices]
names[ordered_indices]
9、squeeze 方法去除多余的轴
>>> a = np.arange(6)
>>> a.shape = (2,1,3)
# 将所有长度为1的维度去除
>>> b = a.squeeze()
b.shape=(2,3)
10、Flatten 数组
a = array([[0,1], [2,3]])
# 返回的是数组的复制,因此,改变 b 并不会影响 a 的值
b = a.flatten()
# a.flat 相当于返回了所有元组组成的一个迭代器, 修改 b 的值会影响 a
b = a.flat
b = a.ravel()
11、对角线
a = np.array([11,21,31,12,22,32,13,23,33], )
a.shape = 3,3
a.diagonal()
# 使用偏移来查看它的次对角线,正数表示右移,负数表示左移
a.diagonal(offset=1)
a.diagonal(offset=-1)
# 获取矩阵相乘对角元素
A = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (5, 5))
B = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (5, 5))
# Slow version
np.diag(np.dot(A, B))
# Fast version
np.sum(A * B.T, axis=1)
# Faster version
np.einsum("ij,ji->i", A, B)
12、toString
a = np.array([[1,2], [3,4]], dtype = np.uint8)
s = a.tostring()
b = np.fromstring(s, dtype=np.uint8)
b
array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=uint8)
from io import StringIO
s = StringIO("""1, 2, 3, 4, 5\n
6, , , 7, 8\n
, , 9,10,11\n""")
a = np.genfromtxt(s, delimiter=",", dtype=np.int)
a = np.genfromtxt(sample_file, delimiter=",", dtype=np.int)
# dataframe其中一列为numpy array
df = pd.read_csv(filename, dtype={'emotion':np.int32, 'pixels':str, 'Usage':str})
df['pixels'] = df['pixels'].apply(lambda text: np.fromstring(text, sep=' '))
13、矩阵生成
# 随机的 3*3*3矩阵
np.random.random((3,3,3))
>>> a = np.array([[1,2,4],
[2,5,3],
[7,8,9]])
>>> A = np.mat(a)
>>> A
matrix([[1, 2, 4],
[2, 5, 3],
[7, 8, 9]])
>>> A = np.mat('1,2,4;2,5,3;7,8,9')
>>> A * A.I # A.I表示A矩阵的逆矩阵
# 产生一个n乘n的单位矩阵
np.eye(3)
np.identity(3)
# 全为1的矩阵
np.ones((10,10))
14、替换最大值
a = np.random.random(10)
a[a.argmax()] = 0
15、类型转换
a = np.arange(10, dtype=np.int32)
a = a.astype(np.float32, copy=False)
16、遍历array
a = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3)
for index, value in np.ndenumerate(a):
print(index, value)
for index in np.ndindex(a.shape):
print(index, a[index])
17、矩阵操作
# 减去每行的均值
x = np.random.rand(5, 10)
y = x - x.mean(axis=1, keepdims=True)
# 对第n列排序
m = np.random.randint(0, 10, (3, 3))
m[m[:,1].argsort()]
# 矩阵互换两行
A = np.arange(25).reshape(5,5)
A[[2,1]] = A[[1,2]]
# SVD
Z = np.random.uniform(0,1,(10,10))
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(Z)
rank = np.sum(S > 1e-10)
# 矩阵内积、外积、和、乘法
A = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 10)
B = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 10)
np.einsum('i->', A) # np.sum(A)
np.einsum('i,i->i', A, B) # A * B
np.einsum('i,i', A, B) # np.inner(A, B)
np.einsum('i,j->ij', A, B) # np.outer(A, B)
18、滑动窗口内求均值
def moving_average(a, n=3) :
ret = np.cumsum(a, dtype=float)
ret[n:] = ret[n:] - ret[:-n]
return ret[n - 1:] / n
a = np.arange(20)
moving_average(a, n=3)
19、数组中最值
# 出现最频繁的数
a = np.random.randint(0, 10, 50)
# bin的数量比a中的最大值大1,每个bin给出了它的索引值在a中出现的次数
np.bincount(a).argmax()
# 取top-k
a = np.arange(10000)
np.random.shuffle(a)
n = 5
# Slow
a[np.argsort(a)[-n:]]
# Fast
a[np.argpartition(-a, n)[:n]]
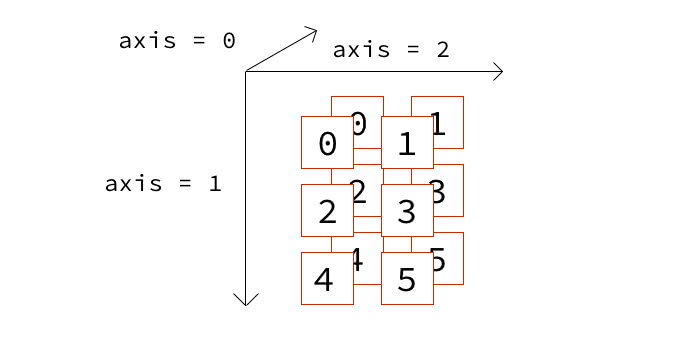
20、np aggr axes
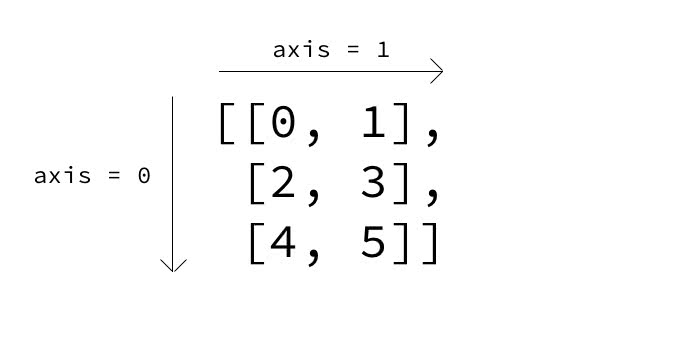
a = np.arange(6).reshape((3, 2))
a
array([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5]])
np.sum(a, axis=0, keepdims=True)
array([[6, 9]])
np.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True)
array([[1],
[5],
[9]])
np.max(a, axis=0, keepdims=True)
array([[4, 5]])
np.max(a, axis=1, keepdims=True)
array([[1],
[3],
[5]])
b = np.array([a, a])
b
array([[[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5]],
[[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5]]])
np.sum(b, axis=0, keepdims=True)
array([[[ 0, 2],
[ 4, 6],
[ 8, 10]]])
np.sum(b, axis=1, keepdims=True)
array([[[6, 9]],
[[6, 9]]])
np.sum(b, axis=2, keepdims=True)
array([[[1],
[5],
[9]],
[[1],
[5],
[9]]])
np.max(b, axis=0, keepdims=True)
array([[[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5]]])
np.max(b, axis=1, keepdims=True)
array([[[4, 5]],
[[4, 5]]])
np.max(b, axis=2, keepdims=True)
array([[[1],
[3],
[5]],
[[1],
[3],
[5]]])
21、多维数组乘法
对于array对象,* 和 np.multiply 函数代表的是数量积,np.dot 和 np.matmul 函数代表矩阵乘法(矢量乘法); 对于matrix对象,* 直接代表矩阵乘法(矢量乘法),np.multiply 函数表示数量积;
tensorflow乘法
1、c = tf.matmul(a, b)
二维tensor相乘 [m, k] x [k, n] = [m, n] 多维tensor相乘 [x, y, m, k] x [x, y, k, n] = [x, y, m, n],并且这里的x, y是支持广播的
2、c = tf.multiply(a, b)
按元素相乘,a, b必须形状相同,支持广播。
3、c = tf.tensordot(a, b, axes=(axes_a, axes_b))
表示任意多维,任意组合形式的矩阵相乘。(axes_a, axes_b)把 a 和 b 的元素的乘积沿着 axes_a 和 axes_b 加和。
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4])
b = tf.constant([2, 3, 4, 5])
c1 = tf.tensordot(a, b, axes=0) # axes=0则按照逐元素挨个相乘
<tf.Tensor: id=195, shape=(4, 4), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 4, 6, 8, 10],
[ 6, 9, 12, 15],
[ 8, 12, 16, 20]], dtype=int32)>
c2 = tf.tensordot(a, b, axes=1) # 表示内积,直接令 axes=1
<tf.Tensor: id=206, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=40>
22、矩阵两两之间的相似性
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
from scipy import sparse
A = np.array([[0, 1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0, 1, 0]])
A_sparse = sparse.csr_matrix(A)
similarities = cosine_similarity(A_sparse)
print('pairwise dense output:\n {}\n'.format(similarities))
#also can output sparse matrices
similarities_sparse = cosine_similarity(A_sparse, dense_output=False)
print('pairwise sparse output:\n {}\n'.format(similarities_sparse))
top_k=3
for i in range(len(similarities)):
sim_arr = similarities[i]
# top_index=np.argsort(sim_arr)[-top_k:]
top_index=np.argpartition(sim_arr, -top_k)[-top_k:]
print(str(list(zip(top_index, sim_arr[top_index]))))
# 协方差
np.cov(A)
# 相关系数
np.corrcoef(A)
23、kNN求解
import numpy as np
from numpy import ndarray
random.seed(5)
def generate_points(n: int=6) -> list[tuple]:
points = []
for i in range(n):
points.append((random.randint(0, 100), random.randint(0, 100)))
return points
def structured_array(points: list[tuple]) -> ndarray:
dt = np.dtype([('x', 'int'), ('y', 'int')])
return np.array(points, dtype=dt)
def np_find_dist(s_array: ndarray) -> ndarray:
size = s_array.shape[0]
a = s_array.reshape(size, 1)
b = s_array.reshape(1, size)
# 广播机制
dist = (a['x'] - b['x'])**2 + (a['y'] - b['y'])**2
return dist
def np_k_nearest(dist: ndarray, k: int) -> ndarray:
k_indices = np.argpartition(dist, k+1, axis=1)[:, :k+1]
return k_indices
def np_main(count: int = 6, top_k: int = 2):
points = generate_points(count)
s_array = structured_array(points)
np_dist = np_find_dist(s_array)
k_indices = np_k_nearest(np_dist, top_k - 1)
# 花式索引
results = [s_array[k_indices[i, :k+1]] for i in range(s_array.shape[0])]
return results, s_array, k_indices, k
results, s_array, k_indices, k = np_main(100, 1)
24、稀疏举例
Coordinate (COO)
COO 格式中每一个元素用一个三元组(行号,列号,数值)表示
from scipy import sparse
rows = np.array([0, 3, 1, 0])
cols = np.array([0, 3, 1, 2])
data = np.array([6, 5, 7, 8])
sparse.coo_matrix((data, (rows, cols)), shape=(4, 4)).toarray()
array([[6, 0, 8, 0],
[0, 7, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 5]])
Compressed Sparse Column (CSC)
CSC是按列存储的稀疏矩阵,其中indptr中的数据代表矩阵中每一列所存的数据在data中的开始和结束的索引,例如indptr为[0, 2, 3, 6],即表示在data中,索引[0, 2)为第一列的数据,索引[2, 3)为第二列的数据,索引[3, 6)为第三列的数据。而indices中的数据代表所对应的data中的数据在其所在列中的所在行数,例如,这里的indices为[0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2],表示在data中,数据1在第0行,数据2在第2行,数据3在第2行,数据4在第0行,数据5在第一行,数据6在第2行。 CSC 适合做矩阵运算以及列切片,在内存中,它的元素是按列存储。
indptr = np.array([0, 2, 3, 6])
indices = np.array([0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2])
data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
sparse.csc_matrix((data, indices, indptr), shape=(3, 3)).toarray()
array([[1, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 5],
[2, 3, 6]])
Compressed Sparse Row (CSR)
CSR是按行来存储的稀疏矩阵,其与CSC类似。indptr中的数据表示矩阵中每一行的数据在data中开始和结束的索引,而indices中的数据表示所对应的在data中的数据在矩阵中其所在行的所在列数。
indptr = np.array([0, 2, 3, 6])
indices = np.array([0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2])
data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
sparse.csr_matrix((data, indices, indptr), shape=(3, 3)).toarray()
array([[1, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
25、numpy array和tensor轴线对比
x = tf.constant([[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]])
tf.reduce_sum(x) # 15
tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=0) # shape=(2,), array([6, 9])
tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=0, keep_dims=True) # shape=(1, 2) array([[6, 9]])
tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=1) # shape=(3,) array([1, 5, 9])
tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=1, keep_dims=True) # shape=(3, 1) array([[1],[5],[9]])
tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=-1) # shape=(3,) array([1, 5, 9])
tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=[0, 1]) # 15
a = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]])
np.sum(a) # 15
np.sum(a, axis=0) # array([6, 9])
np.sum(a, axis=0, keepdims=True) # array([[6, 9]])
np.sum(a, axis=1) # array([1, 5, 9])
np.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True) # array([[1],[5],[9]])
np.sum(a, axis=-1) # array([1, 5, 9])
26、Numexpr优化
import numpy as np
from numpy import ndarray
import numexpr as ne
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=4000)
def generate_ndarray(rows: int) -> np.ndarray:
result_array = rng.random((rows, 1))
return result_array
arr = generate_ndarray(10)
def numexpr_to_binary(np_array: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
# N * 1 -> N
temp = np_array[:, 0]
temp = ne.evaluate("where(temp<0.5, 0, 1)")
# N -> N * 1
return temp[:, np.newaxis]
arr = generate_ndarray(10)
result = numexpr_to_binary(arr)
mapping = np.column_stack((arr, result))
mapping