Java 8引入了CompletableFuture<T>以及它的接口CompletionStage<T>作为对Future<T>的增强,它可以让你使用回调驱动的方式表达不同任务的信息流。CompletableFuture用来定义单个任务事件的计算。本文主要介绍其用法以及常见的工具方法。
CompletableFuture<T> API
1、 异步操作
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> runnable.run()),返回CompletableFuture<Void>;CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> supplier.get()),返回CompletableFuture<T>
2、 链式异步操作
cf.thenRun(() -> runnable.run()),返回CompletableFuture<Void>;cf.thenAccept(t -> consumer.accept(t)),返回CompletableFuture<Void>;cf.thenApply(t -> function.apply(t)),返回CompletableFuture<R>
3、 异步 vs. 同步
| 同步 | 异步 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
allOf |
N/A | 所有的CompletableFuture都执行完后执行计算 |
anyOf |
N/A | 当任意一个CompletableFuture执行完后就会执行计算 |
completedFuture |
N/A | 返回一个已经计算好的CompletableFuture |
exceptionally |
N/A | 当原始的CompletableFuture抛出异常的时候,就会触发这个CompletableFuture的计算,调用fn计算值 |
handle |
handleAsync |
生成新的计算结果,有whenComplete和转换的两个功能 |
runAfterBoth |
runAfterBothAsync |
两个CompletionStage都完成计算之后,再执行一个Runnable,Runnable不使用这个计算结果。 |
runAfterEither |
runAfterEitherAsync |
等待第一个完成任务CompletableFuture |
acceptEither |
acceptEitherAsync |
当任意一个CompletionStage完成的时候,消费者action就会被执行 |
applyToEither |
applyToEitherAsync |
当任意一个CompletionStage完成的时候,fn会被执行,返回值作为新的CompletableFuture<U>的计算结果 |
| N/A | runAsync |
以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数 |
| N/A | supplyAsync |
以Supplier<U>函数式接口类型为参数 |
thenApply |
thenApplyAsync |
生成新的计算结果,CompletableFuture<T>转换成CompletableFuture<U> |
thenRun |
thenRunAsync |
纯消费,执行Action,不使用CompletableFuture计算的结果 |
thenAccept |
thenAcceptAsync |
纯消费,执行Action,不返回新的计算值,用于添加回调 |
thenAcceptBoth |
thenAcceptBothAsync |
组合另外一个异步的结果 |
thenCombine |
thenCombineAsync |
复合另外一个CompletionStage的结果 |
thenCompose |
thenComposeAsync |
新CompletableFuture组合原来的CompletableFuture和函数返回的CompletableFuture |
whenComplete |
whenCompleteAsync |
计算结果完成时的处理 |
- thenApply:等待并转化future
- thenAccept、thenRun:监听future完成
- thenCompose:相当于flatMap,避免CompletableFuture<CompletableFuture
> - thenCombine:组合两个future,有返回值
- thenAcceptBoth:组合两个future,没有返回值
- applyToEither:取2个future中最先返回的,有返回值
- acceptEither:取2个future中最先返回的,无返回值
thenApply与handle方法的区别:handle方法会处理正常计算值和异常,因此它可以屏蔽异常,避免异常继续抛出;thenApply方法只是用来处理正常值,因此一旦有异常就会抛出。
anyOf返回值的计算结果是其中一个CompletableFuture的计算结果,applyToEither返回值的计算结果要经过fn处理。
提示:下图图片较大,右击图片,在新标签页打开查看图片。
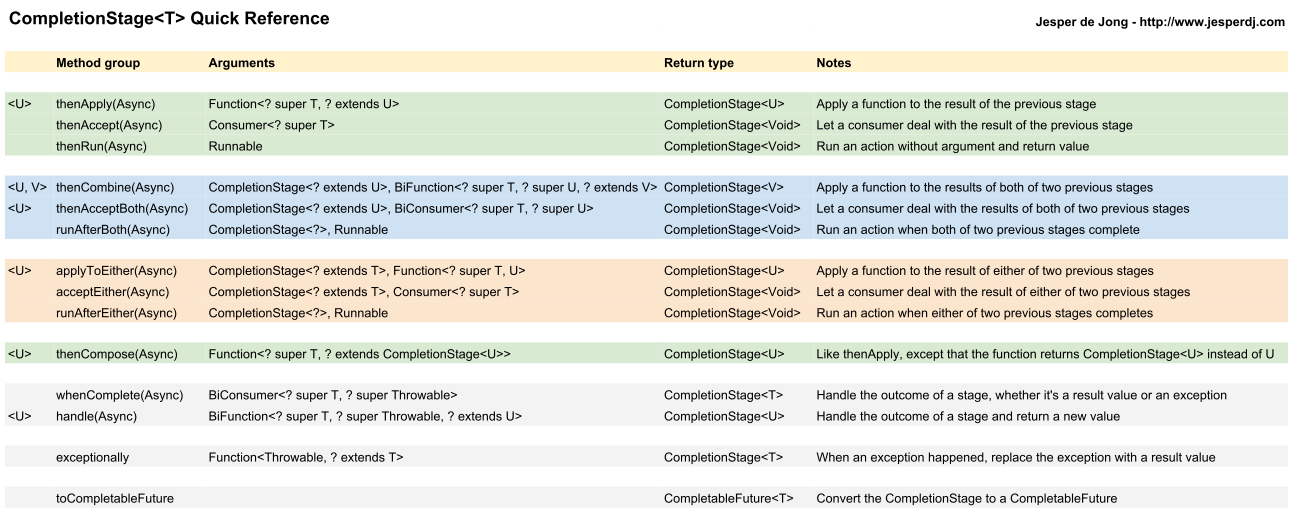
从上图API的分类来看,方法的命名有2点规律:
1、什么东西触发了stage
then开头的方法:当一个单独的stage完成时,添加另一个要触发的stage;- 包含
both的方法:当前面两个stage同时完成时,添加另一个要触发的stage; - 包含
either的方法:当前面两个stage有一个完成,添加另一个要触发的stage;
2、计算是否传入参数和返回结果
- 包含
apply的方法:接收一个Function,该Function一个参数(前一个stage的结果)和返回一个结果(下一个stage的参数); - 包含
accpet的方法:接收一个Consumer,该Consumer接受一个参数,不返回结果; - 包含
run的方法:接收一个Runnable,该Runnable不需要参数和返回结果;
创建已经完成的CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message");
assertTrue(cf.isDone());
assertEquals("message", cf.getNow(null));
运行异步的Stage
CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
});
在前一个stage上施加函数
// 同步
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApply(s -> {
assertFalse(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
return s.toUpperCase();
});
assertEquals("MESSAGE", cf.getNow(null));
// 异步
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApplyAsync(s -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
return s.toUpperCase();
});
assertNull(cf.getNow(null));
assertEquals("MESSAGE", cf.join());
消费前一个Stage的结果
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
// 同步
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("thenAccept message")
.thenAccept(s -> result.append(s));
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
// 异步
CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("thenAcceptAsync message")
.thenAcceptAsync(s -> result.append(s));
cf.join();
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
在两个完成的stage中取任意一个stage结果施加函数
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s));
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf1.applyToEither(
CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
s -> s + " from applyToEither");
assertTrue(cf2.join().endsWith(" from applyToEither"));
在两个完成的stage中任意一个stage结果消费
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.acceptEither(CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
s -> result.append(s).append("acceptEither"));
cf.join();
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.toString().endsWith("acceptEither"));
在两个stage都完成后执行Runnable
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(String::toUpperCase).runAfterBoth(
CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(String::toLowerCase),
() -> result.append("done"));
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
在BiConsumer中接受两个stage的结果
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(String::toUpperCase).thenAcceptBoth(
CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(String::toLowerCase),
(s1, s2) -> result.append(s1 + s2));
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", result.toString());
两个stage的结果施加BiFunction
String original = "Message";
// 同步
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
(s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.getNow(null));
// 异步
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
(s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.join());
组合CompletableFutures
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCompose(upper -> CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original).thenApply(s -> delayedLowerCase(s))
.thenApply(s -> upper + s));
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.join());
错误处理
1、 处理异常返回默认值
CompletableFuture<Integer> x = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (failure) {
throw new RuntimeException("Oops, something went wrong");
}
return 42;
});
// Note that tryX and x are of same type.
CompletableFuture<Integer> tryX = x.exceptionally(ex -> -1);
2、 处理异常并转换
CompletableFuture<Integer> x = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (failure) {
throw new RuntimeException("Oops, something went wrong");
}
return 42;
});
CompletableFuture<HttpResponse> tryX = x.handle((value, ex) -> { // Note that tryX and x are of different type.
if (value != null) {
return new HttpResponse(200, format("{\"value\": %s}", value));
} else {
return new HttpResponse(500, format("{\"error\": \"%s\"}", ex.getMessage()));
}
});
3、 处理异常并传递
CompletableFuture<Integer> x = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (failure) {
throw new RuntimeException("Oops, something went wrong");
}
return 42;
});
// Note that tryX and x are of same type. This CompletableFuture acts as an invisible "decorator".
CompletableFuture<Integer> tryX = x.whenComplete((value, ex) -> {
if (value != null) {
System.out.println("Result: " + value);
} else {
System.out.println("Error code: -1. Root cause: " + ex.getMessage());
}
});
链式使用
result = (x + 1) + y
CompletableFuture<Integer> x1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> compute(1));
CompletableFuture<Integer> x2 = x1.thenApply(x -> add(x, 1));
CompletableFuture<Integer> y = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> compute(2));
CompletableFuture<Integer> r = x2.thenCombine(y, (i, j) -> add(i, j));
try { println("Result: " + r.get()); } catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
(i, j) -> add(i, j)将来自y和x2的Integer作为输入并进行转换得到最终结果。
优化超时
CompletableFuture.get()阻塞主线程直到CompletableFuture计算完成。一般应该给get指定超时时间,如r.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)。
1、 回调
使用thenAccept并在返回结果可用时提供回调计算,如:
r.thenAccept(result -> System.out.println("The result is: " + result));
2、 非阻塞方法确定超时
使用acceptEither或者applyToEither。
r.acceptEither(timeoutAfter(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS),
result -> System.out.println("The result is: " + result));
public <T> CompletableFuture<T> timeoutAfter(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
CompletableFuture<T> promise = new CompletableFuture<T>();
delayer.schedule(() -> promise.completeExceptionally(new TimeoutException()), timeout, unit);
return promise;
}
delayer的类型为ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
3、 Java 9改进
Java 9引入了orTimeout和completeOnTimeOut解决超时问题。
public CompletableFuture<T> orTimeout(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
public CompletableFuture<T> completeOnTimeout(T value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
r.orTimeout(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.whenComplete((result, error) -> {
if (error == null) {
System.out.println("The result is: " + result);
} else {
System.out.println("Sorry, we could not return you a result");
}
});
CompletableFuture::join
/**
* Returns a new {@link CompletableFuture} which completes to a list of all values of its input
* stages, if all succeed. The list of results is in the same order as the input stages.
*
* If any of the given stages complete exceptionally, then the returned future also does so,
* with a {@link CompletionException} holding this exception as its cause.
*/
public static <T> CompletableFuture<List<T>> allAsList(
Collection<? extends CompletionStage<? extends T>> stages) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final CompletableFuture<? extends T>[] all = new CompletableFuture[stages.size()];
// traditional for-loops instead of streams here for performance reasons
for (int i = 0; i < stages.size(); i++) {
all[i] = stages.get(i).toCompletableFuture();
}
return CompletableFuture.allOf(all)
.thenApply(ignored -> {
final List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(all.length);
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
result.add(all[i].join());
}
return result;
});
}
// example
List<String> values = asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = values.stream().map(CompletableFuture::completedFuture).collect(toList());
CompletableFuture<List<String>> joined = allAsList(futures);
/**
* Collect a stream of {@link CompletionStage}s into a single future holding a list of the
* joined entities.
* <pre>{@code
* collection.stream()
* .map(this::someAsyncFunc)
* .collect(joinList())
* .thenApply(this::consumeList)
* }</pre>
*/
public static <T, S extends CompletionStage<? extends T>>
Collector<S, ?, CompletableFuture<List<T>>> joinList() {
return Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), CompletableFutures::allAsList);
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link CompletableFuture} which completes to a list of values of those input
* stages that succeeded. The list of results is in the same order as the input stages. For failed
* stages, the defaultValueMapper will be called, and the value returned from that function will
* be put in the resulting list.
*/
public static <T> CompletableFuture<List<T>> successfulAsList(
List<? extends CompletionStage<T>> stages,
Function<Throwable, ? extends T> defaultValueMapper) {
return stages.stream()
.map(f -> f.exceptionally(defaultValueMapper))
.collect(joinList());
}
// example 遇到异常按默认值处理
List<CompletableFuture<String>> input = Arrays.asList(
completedFuture("a"),
exceptionallyCompletedFuture(new RuntimeException("boom")));
CompletableFuture<List<String>> joined = CompletableFutures.successfulAsList(input, t -> "default");
CompletableFuture优雅处理异常
private static final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler =
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setDaemon(true).setNameFormat("failAfter-%d").build());
public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> failAfter(Duration duration) {
final CompletableFuture<T> promise = new CompletableFuture<>();
scheduler.schedule(() -> {
final TimeoutException ex = new TimeoutException("Timeout after " + duration);
return promise.completeExceptionally(ex);
}, duration.toMillis(), MILLISECONDS);
return promise;
}
public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> within(CompletableFuture<T> future, Duration duration) {
final CompletableFuture<T> timeout = failAfter(duration);
return future.applyToEither(timeout, Function.identity());
}
final CompletableFuture<Response> responseFuture = within(asyncCode(), Duration.ofSeconds(1));
responseFuture.thenAccept(this::send)
.exceptionally(throwable -> {
log.error("Unrecoverable error", throwable);
return null;
});
定时轮训外部资源
/**
* Polls an external resource periodically until it returns a non-empty result.
*
* <p> The polling task should return {@code Optional.empty()} until it becomes available, and
* then {@code Optional.of(result)}. If the polling task throws an exception or returns null,
* that will cause the result future to complete exceptionally.
*
* <p> Canceling the returned future will cancel the scheduled polling task as well.
*
* <p> Note that on a ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor the polling task might remain allocated for up
* to {@code frequency} time after completing or being cancelled. If you have lots of polling
* operations or a long polling frequency, consider setting {@code removeOnCancelPolicy} to true.
* See {@link java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor#setRemoveOnCancelPolicy(boolean)}.
*
* @param pollingTask the polling task
* @param frequency the frequency to run the polling task at
* @param executorService the executor service to schedule the polling task on
* @param <T> the type of the result of the polling task, that will be returned when
* the task succeeds.
* @return a future completing to the result of the polling task once that becomes available
*/
public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> poll(
final Supplier<Optional<T>> pollingTask,
final Duration frequency,
final ScheduledExecutorService executorService) {
final CompletableFuture<T> result = new CompletableFuture<>();
final ScheduledFuture<?> scheduled = executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(
() -> pollTask(pollingTask, result), 0, frequency.toMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
result.whenComplete((r, ex) -> scheduled.cancel(true));
return result;
}
private static <T> void pollTask(
final Supplier<Optional<T>> pollingTask,
final CompletableFuture<T> resultFuture) {
try {
pollingTask.get().ifPresent(resultFuture::complete);
} catch (Exception ex) {
resultFuture.completeExceptionally(ex);
}
}